Decision Analytics vs. Monte Carlo Simulation
Critical business decisions deserve the most rigorous approach to analyzing potential risks and enumerating possible alternatives. While Monte Carlo simulation provides a quick method for assessing risk and helping the user make a go/no go decision, it does not provide a system for structuring a decision problem and mapping out alternatives.
We encourage you to request a FREE 21-day trial license of the DPL Professional software and see how a Decision Analytic Approach may enhance the quality of your strategic business decisions:
The Limitations of Monte Carlo Simulation
Monte Carlo simulation is limited in that it requires a pre-specified decision rule of thumb be applied regardless of the situation. While this rule of thumb may make sense in a given scenario, there is no guarantee that it is appropriate across a range of scenarios. Monte Carlo takes a less rigorous approach than Decision Analysis which allows for a more comprehensive framework for structuring uncertainties, defining dependencies and explicitly considering alternatives in order to arrive at the most well-conceived decision.
| Decision Analysis | Monte Carlo | |
|---|---|---|
| DECISIONS
|
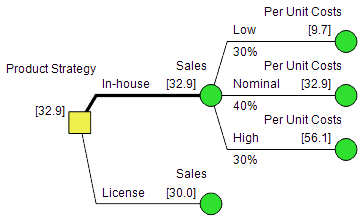
Decisions are modelled explicitly (e.g., we can build, abandon, or wait). | Most decisions are modelled as rules (e.g., =IF(A42>B42,C42,0).) |
| BOTTOM LINE: It's about the decisions. | ||
| UNCERTAINTIES
|
Most uncertainties are modeled with discrete outcomes. Probabilities and values are assessed. | Most uncertainties are modeled with common statistical distributions. Distribution parameters are assessed. |
| BOTTOM LINE: Decision makers have more intuition for specific outcomes than for things like variance and skewness. | ||
| DEPENDENCIES
|
Dependence between uncertainties is usually handled explicitly ("if we know natural gas prices are high the likelihood changes to..."). | Dependence between uncertainties is usually handled with a correlation coefficient. (In practice, it is often ignored.) |
| BOTTOM LINE: Even technical people have little intuition for correlation coefficients. | ||
| VALUE OF INFORMATION
|
The importance of an uncertainty (& the value of learning more about it) can be calculated and shown in a tree. | Value of information can't be calculated directly (no explicit modelling of decisions). |
| BOTTOM LINE: Value of information has relevance to real world actions and can be used to determine when to move forward. | ||
| SOLUTION METHOD
|
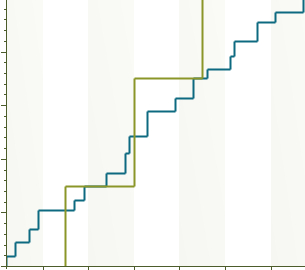
Results come from a Policy Tree™ every scenario can be inspected and the Policy Tree™ provides a "strategic road map" for making decisions and managing value going forward. | Results come from a number of equally likely random draws of the input distributions. |
| BOTTOM LINE: Portions of the tree are meaningful and can build understanding. With Monte Carlo, each draw is independent, results are only stable for a very large number of draws. | ||
| RESULTS
|
In addition to the Policy Tree™ the other main result is a Risk Profile showing the overall range of outcomes. Numerous sensitivity analyses are available. | Pretty much just an output distribution. |
| BOTTOM LINE: An outcome probability distribution is usually not enough to give a decision maker confidence that a thorough analysis has been performed and a decision can be made. | ||